Unity CMD
About#
This task allows for full control over the arguments passed to the Unity command line. It's aimed at advanced users with specific requirements. For most use cases and users the use of the other provided tasks is recommended as it provides a guided and targeted experience. You can find the task when editing your pipeline by searching for the name Unity CMD. In short: use this task only if you know what you are doing.
Inputs#
This task supports input variables for configuration.
unityEditorsPathMode#
For the task to run successfully it needs to know where Unity installations are located at on the agent. This input lets you configure, where the task should look for installations.
Required: Yes
Default Value: unityHub
Options:#
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| unityHub | Uses the Unity Hub default installation path. |
| environmentVariable | Expects an environment variable UNITYHUB_EDITORS_FOLDER_LOCATION to exist on the agent and specifying where to find editor installations. |
| specify | Let's you specify a custom path where to lookup editor installations using the input customUnityEditorsPath. |
customUnityEditorsPath#
If you are using a custom buld agent you may want to specify a custom path to specify where to look for Unity installations. This input lets you do that.
Make sure to set unityEditorsPathMode to specify for this input to take effect.
Required: Yes, if unityEditorsPathMode set to specify
Default Value: -
unityProjectPath#
Enter the directory path to the Unity project. If no value is entered, the project is assumed to be in the repository root.
Required: No
Default Value: -
cmdArgs#
Specify command line arguments to pass to the Unity process when running the task.
warning
The task will set -batchmode, -projectPath and -logfile for you and you shouldn't specify them in your custom command line arguments. These three arguments are currently required to be always set for the task to work as designed.
Required: Yes
Default Value: -
Options:#
Check the official Unity command line documentation for options.
Outputs#
This task provides output variables.
logsOutputPath#
Path to the Unity editor log files generated while executing the task. Use this e.g. to upload logs in case of a failure.
How to use#
Here's a simple example of how to use and define the task in your pipeline. For more examples, check the Examples Collection.
YAML#
In the simple YAML example below we are definiing the task a step in the pipeilne using - task: UnityCMDTask@1. We are also giving the task a reference name using name: unitycmd, so we can use it to refernce the output variables of the task in other tasks of the pipeline. E.g. we can output the value of the logsOutputPath output variable to the console using echo $(unitycmd.logsOutputPath). For cmdArgs we specify that Unity should target the standalone platform and execute our custom build script MyBuildTools.BuildProject to perform the build.
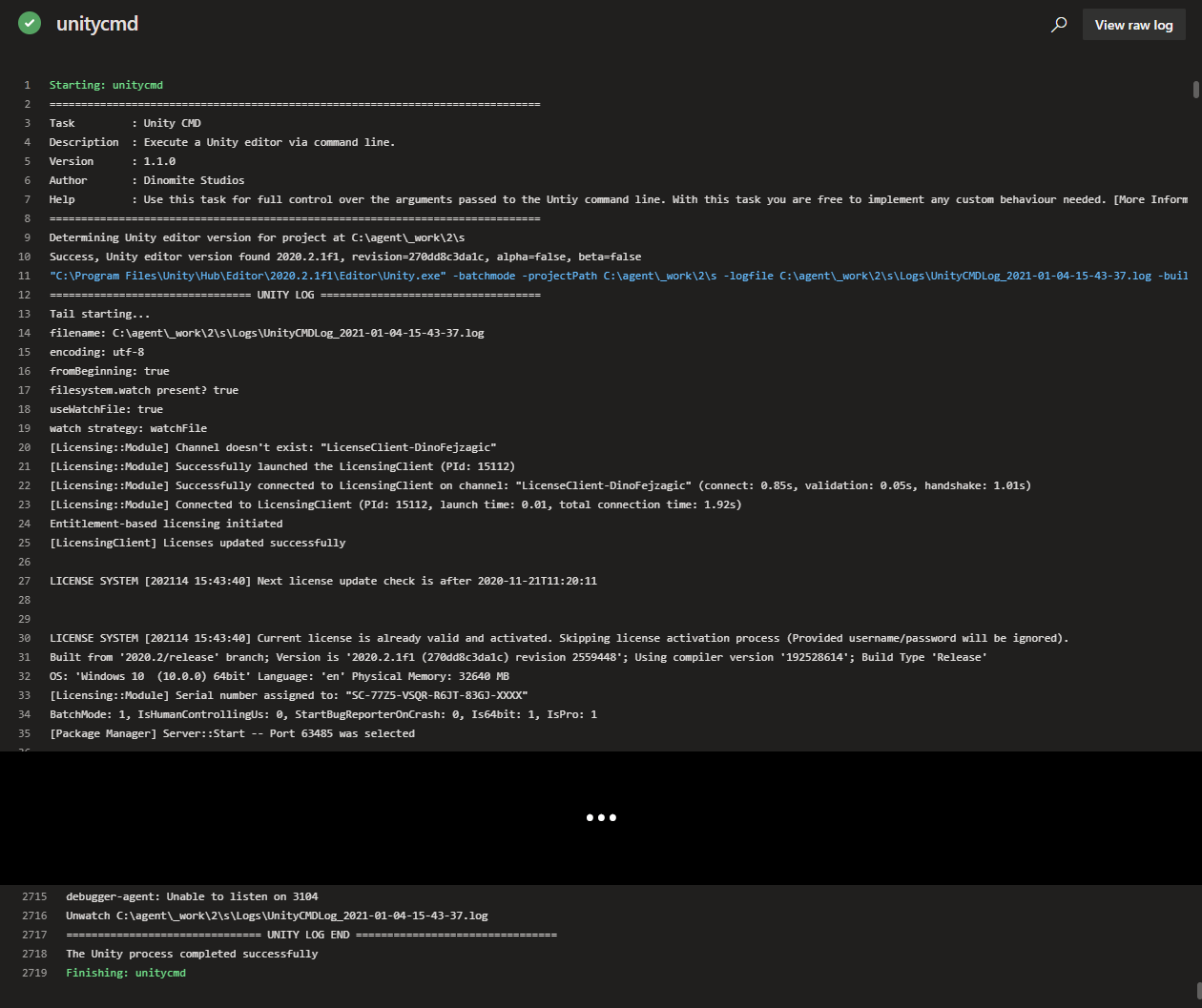
Classic Pipeline Editor#
The classic (visual) editor for Azure Pipelines provides input fields for configuring the task. In the simple example below, we set Unity editors location to use the default Unity Hub installation path to lookup installed Unity editor versions on the agent running our pipeline. We are also leaving the Unity project path field empty, since we know our Unity project is in the repository root. For Command line arguments we specify that Unity should target the standalone platform and execute our custom build script MyBuildTools.BuildProject to perform the build. We are also assigning a Reference name to the task, so we can use it to refernce the output variables in the variables list in other tasks of the pipeline. E.g. to get the value of the logsOutputPath output variable and insert it into any other input field of a task we can then use $(unitycmd.logsOutputPath).
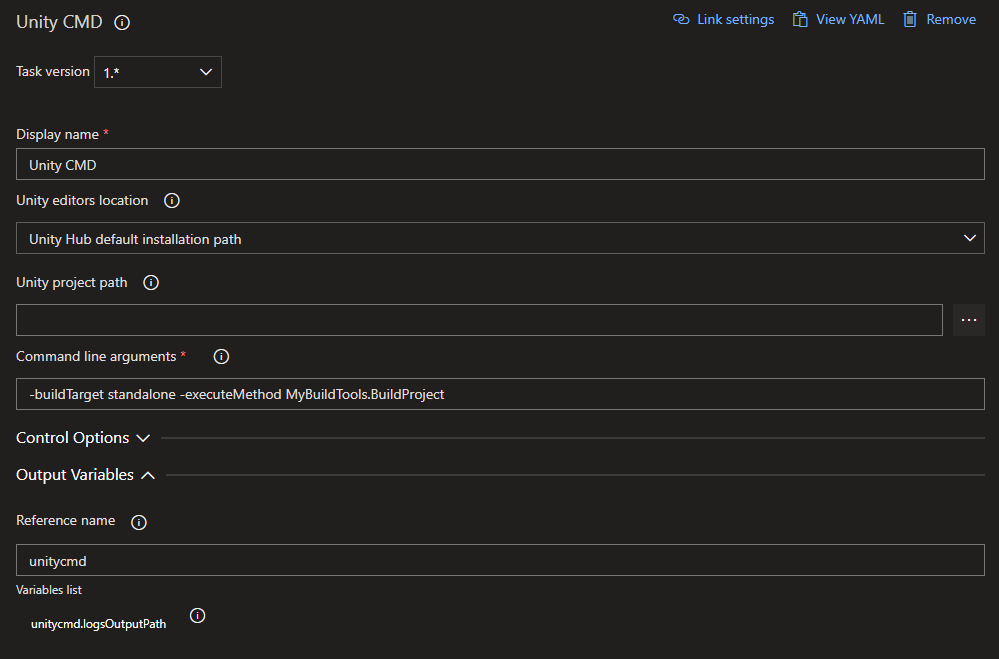
Log#
When run and successful the task will provide log output similar to this: